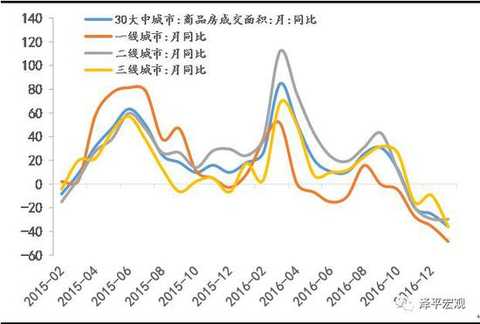
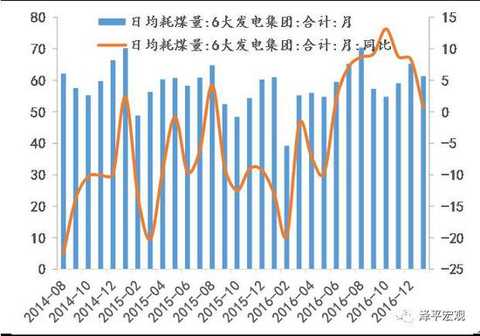
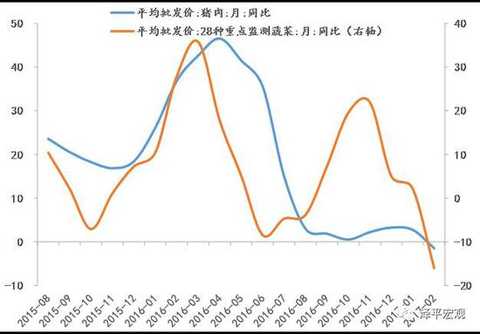
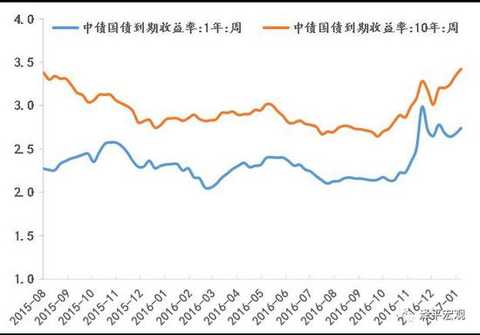
[Zeping Macro] We are in the process of raising interest rates: the path and the impact - the high frequency judgment Text: Founder Macro Ren Zeping Contact: Lu Liangliang Core point of view: We are in the midst of a round of interest rate hikes. This process is gradual: since the 229 RRR cut in 2016, the central bank has no obvious easing measures, and more liquidity through open market operations, from loose to neutral. After half a year, at the end of August 2016, restarted the 14-day reverse repurchase, and then restarted the 28-day reverse repurchase, increased the MLF operation, shortened the lock, lengthened the period, and increased the cost of capital, equivalent to the implicit rate hike. It marks that the monetary policy has turned from neutral to tight; in January 2017, the central bank officially raised the MLF semi-annual and one-year interest rates, marking the interest rate hike from recessive to dominant; on February 3, the central bank once again reversed the repo and SLF. The interest rate hike indicates that the short-term and long-end interest rates have been raised. The 10-year bond yield has risen from the low of 2.64% in mid-August 2016 to the current 3.42%. The interest rate signal is further clear, so the central bank has actually Raise interest rates. Therefore, we need to observe the future from the perspective of the rate hike cycle: Why raise interest rates? What is the future rate hike path? What impact will it have on the economy and the big assets? Why raise interest rates? We believe that the policy goal is to prevent risk and deleverage. In July 2016, the Politburo meeting proposed “inhibiting the asset bubbleâ€. In October, the Politburo meeting emphasized “focusing on restraining asset bubbles and preventing economic and financial risksâ€. In December, the Central Economic Work Conference clarified that the policy tone shifted from stable growth to risk prevention and reform. . Since the second half of 2016, the debt market has been de-lost, real estate regulation and control, and the off-balance sheet wealth management business has been included in the macro-prudential assessment, and the new regulations on insurance and insurance supervision are mainly to implement the policy orientation of anti-risk de-leveraging. At the same time, since the beginning of 2016, the economic L-type stabilization, inflation expectations, housing prices soaring, etc. have provided fundamental support, and the political transition in 2017 needs to maintain stability. The narrowing of the external share made the central bank regain the initiative to supply the base money and regulate liquidity, so the central bank took the lead in adjusting the interest rate, duration and quantity of open market operations. What is the future rate hike path? At present, it is mainly to adjust the operating rate, term and quantity of the open market. Will it be upgraded to adjust the deposit and loan interest rate and reserve ratio in the future? Since the current policy goal is to prevent risks and deleverage rather than to curb overheating and inflation, the funds in the financial sector such as the real estate market, the bond market, and emerging insurance are “disconnected to the virtualâ€, “selling money with money†and unreasonable additions. Leverage behavior, rather than infrastructure investment, manufacturing investment, consumption, exports and other real economic sectors, and the Central Economic Work Conference clearly put forward "emphasis on revitalizing the real economy" and promote the "de-funding" of funds. At the same time, considering that the current economic stabilization is not strong, real estate vehicles have been adjusted back, and overall inflation is moderate, the central bank does not have the conditions and demands to substantially increase the deposit and loan interest rate unless the economic or inflation situation exceeds expectations. Of course, the current interest rate market is not completely divided. In today's interest rate marketization, the interest rate transmission mechanism will play a certain role in the money market, bond market, deposit and loan market, and stock market. In the future, the financing cost of the real economy will rise to varying degrees. . In terms of the duration of the rate hike, the past liquidity tightening cycle indicates that it generally lasts at least one year to one and a half years, and will last at least until mid-2017 if it is counted from August 2016. From the money shortage in 2010 to the money shortage in 2013, and then to the money shortage in 2016, roughly one year of reincarnation, all of which are caused by the tightening of the liquidity tightening cycle: economic downturn - currency discharge - stimulating real estate, housing prices skyrocketing - currency Excessive realism, excessive prosperity in the financial market - real estate investment bottomed out, the economy stabilized in the short-term - macro-control tightening, anti-risk de-leverage - money shortage, debt disaster, stock market crash, devaluation, local feathers - economic down again, currency by It is expected to heat up. The depreciation of the exchange rate at the beginning of 2016-2017, the outflow of capital, the regulation after the skyrocketing housing prices, the money shortage, and the debt disaster are all the shocks caused by the liquidity tightening cycle. What impact will it have on the economy and the big assets? The impact of interest rate hikes on the bond market is the most direct, but the impact on the real estate market is likely to be the biggest, which will further increase the possibility of a double dip in the economy in the second quarter and an inflationary correction. Under the interest rate hike cycle, high leverage and interest rate sensitive sectors will be hit hard, such as bond markets, real estate, cyclical industries in the real estate chain, and aviation. Interest rate hikes are less affected by low leverage and interest rate neutral sectors, such as agriculture, food and beverage, medicine, electricity, and road and rail transportation. Since this interest rate hike is to adjust the open market operating rate rather than the loan interest rate, the impact on the bank is generally negative, but considering the supply side clearing to drive corporate earnings recovery and the decline in non-performing rate, the negative impact of interest rate hike is expected to pass the fundamentals. digestion. The impact of interest rate hikes on the RMB exchange rate is positive, and interest rate offsets have been added. However, the basic problems such as over-estimation caused by currency over-issuance and the mismatch of funds to the decline in total factor productivity brought by real estate have not been resolved. Therefore, under the interest rate hike cycle, our ranking of major assets is: gold > price increases in the stock market and reform benefit sectors > goods that are cleared out > bonds > periodic goods in the real estate chain > real estate. Since we first recommended gold in the market in December 2016, gold has clearly outperformed. In the process of raising interest rate cycle and liquidity ebb, we should make steady investment and not swim naked. Affected by real estate regulation and the Spring Festival holiday, the volume of commercial housing in the second half of January fell sharply. Affected by the 17-year purchase tax adjustment and the Spring Festival holiday, the growth rate of passenger car wholesale and retail sales slowed down. During the Spring Festival, there has been a structural change in Chinese consumption. In addition to the traditional sales of new year's goods and gold jewelry, green smart goods and Internet consumption have become a new trend. Tourism and film consumption have reached new heights. During the Spring Festival, industrial production slowed down, and coal consumption in January 6 fell by 7.7 percentage points from the previous month. Steel prices in January were 67.4% year-on-year, down from 76.5% in December. Cement prices remained stable. The oil price rose, the color trend diverged, the copper price increased and the aluminum and zinc price increased. Before the Spring Festival, the price of vegetables and meat prices rose significantly. The US dollar weakened and the RMB exchange rate was stable in the short term. Risk warning: interest rate hikes and liquidity tightening; exchange rate depreciation and capital outflows; real estate regulation; Fed rate hike; reforms lower than expected; debt risk. text 1. Downstream: the trading of commercial housing in the Spring Festival slipped, and the wholesale and retail of passenger cars went down. Affected by the Spring Festival holiday, the volume of commercial housing in the second half of January fell sharply. In the fourth week of January, the transaction area of ​​commercial housing in 30 large and medium-sized cities fell by 43.0%. The average daily area of ​​commercial housing transactions in the first two days of February continued to fall by 94.9%. As of January 31, the sales area of ​​the city's real estate in January was -35.6%, down from -25.1% in December. As of the New Year's Eve (January 26), 30-city real estate sales were -24.9% year-on-year, lower than the -18.2% of the week before the holiday but slightly better than the December value. In terms of regions, the first, second and third cities were -36.7%, -16.8% and -28.3%, respectively, down by 1.3, up by 12.5 and down by 18.9 percentage points from -35.4%, -29.3% and -9.4% in December. In the second half of January, the land purchase area also declined. The land transaction area of ​​the 100 largest cities was -50.9%, and the land area before the holiday was only 5.18 million square meters, mainly concentrated in the second and third tier cities, and the first tier cities sold 60,000 square meters of land. Affected by the 17-year purchase tax adjustment and the Spring Festival holiday, the number of passenger car wholesale and retail sales decreased, and the growth rate slowed down. According to data from the National Federation of Passengers, the growth rate of retail sales of passenger cars in the third week of January was relatively low. The wholesale volume was 64,000 units per day, an increase of 2%, down 16% from last week. The retail sales of passenger cars was 68,000, with a growth rate of 2%, down 17 percentage points from the second week. As of the third week, the growth rate was 6% year-on-year, which was 3.1 percentage points lower than the growth rate of 9.1% in December. The Spring Festival Golden Week data shows structural changes in Chinese consumption. During the 2017 Spring Festival Golden Week, the national retail and catering enterprises achieved sales of about 840 billion yuan, a year-on-year increase of 11.4%; according to the data released by the Ministry of Commerce on February 2, in addition to the traditional new year and the "chicken concept" of gold and silver jewelry In pursuit of the pursuit, green smart goods sales are hot. The “Internetization†of consumption is also a clear trend, and online ordering and online shopping have become new fashions. During the "New Year's Day" this year, Tmall's turnover increased by 42%, and Jingdong's new year sales increased by more than 90%. Tourism and film consumption during the Spring Festival also hit new highs. During the Spring Festival, the country received a total of 344 million tourists, a year-on-year increase of 13.8%, total tourism revenue of 42.33 billion yuan, an increase of 15.9%; the national total box office total of 3.34 billion yuan, breaking the box office record of the same period last year, an increase of 10.0%. The overall demand for textiles and clothing is weak. The Keqiao Textile Index was 1.11% yoy in January, down from 1.21% in the previous week. It was flat in December of 16 years. The raw material and grey cloth prices increased by 3.7% and 1.0% respectively in January, down from 3.8% last week. 1.4%, but still higher than 2.3% and 0.3% in December; the prices of finished products represented by home textiles and apparel fabrics were -0.18% and 0.05%, respectively, down 0.85 and 0.58 percentage points from December. Export demand continued to weaken. The Shanghai Container Freight Index (SCFI) grew by 47.5% year-on-year in January, weaker than the previous value of 48.4% and December's 47.9% year-on-year; the China Container Freight Index (CCFI) was 10.4% year-on-year in January, higher than the previous value of 9.1%. The growth rate was 1.9 percentage points higher than that in December. This round of export recovery will benefit from the depreciation of the RMB and the improvement of the external demand environment. In the later period, we must be alert to the trade war with China after Trump took office. 2, the middle reaches: power consumption coal consumption fell slightly, steel prices rose cement prices stable In the fourth week of January, the average daily coal consumption of the six major power generation groups decreased by 21.0% from the previous week, down 18.5 percentage points from the previous week. As of January 31, the average daily coal consumption of the six major power generations this month was 613,000 tons, down from last week, down from 620,800 tons in the same period in December. Coal consumption in January increased slightly by 0.6% year-on-year, down 7.7 percentage points from the 8.3% in December. In late January, affected by the Spring Festival, industrial production slowed down. In the second half of January, rebar prices stabilized. Compared with the price on January 17, the price dropped slightly by 0.1% on the last day before the holiday, and rose slightly by 0.1% on the first day after the holiday. The price in January was 67.4%, up from last week. 0.9 points, down from 76.5% in December. Market inventories increased sharply during the holiday season, and rebar inventories rose by 37.6% year-on-year in January, up from 16.6% in December. Cement prices remain stable. In the fourth week of January, the national cement price index fell slightly by 0.19% from the previous week, and fell by -0.3% from the first week of February, with little change. Cement prices in January were 29.5% year-on-year, unchanged from the previous year, up from 28.6% in December. According to grassroots research data, the sales volume of excavators remained optimistic in January 2017. Although it was disturbed by the Spring Festival holiday, high growth can still be sustained. The initial growth rate of the industry is between 70% and 80%, and the sales growth of leading enterprises is 100. %about. 3. Upstream: oil prices are rising, copper prices are rising and aluminum and zinc are falling. At the FOMC meeting on February 2, Federal Reserve Chairman Yellen announced that the federal funds rate would remain unchanged and did not give a clear signal of the timing of the next rate hike. The US dollar index fell, once again fell below the 100 mark, the lowest fell to 99.4292. In January, the US dollar index has fallen 2.6%, the worst monthly performance since 2011. The US dollar index fell 0.7% this week, compared with 2.8% in February, up from 2.3% in January. This week, CRB Industrial Raw Materials Index was 0.3% MoM, compared with 20.8% in February, down from 22.5% in January and 23.1% in December. The South China Industrial Products Index was -3.6%, compared with 65.2% in February, down from 71.1% in January and 73.4% in December. The South China Agricultural Products Index was 0.0%, compared with 24.2% in February, up from 22.7% in January. And December was 23.6%. This week, Brent crude oil prices rose by 2.7% month-on-month, compared with 69.1% in February, down from 73.5% in January. The growth rate of non-ferrous metals has slowed down. LME copper prices were 1.0% on a week-on-week basis, compared with 28.8% in February, up from 28.6% in January. LME aluminum prices were -0.8% on a week-on-week basis, compared with 18.2% in February, down from 21.0% in January. LME zinc prices were 3.2% on a week-on-week basis, compared with 66.6% in February, down from 79.4% in January. Domestic and international freight price trends are different. This week, the Baltic Dry Index (BDI) fell by 6.9% month-on-month and 153.5% year-on-year in February, significantly higher than January's 134.8% year-on-year. China's coastal dry bulk freight index (CCBFI) decreased by 1.3% from the previous month, compared with 12.0% in February, down 2.9 and 8.2 percentage points from January and December respectively. 4. Price: food prices rise during the Spring Festival The 2017 Spring Festival is January 28, and the 2016 Spring Festival is February 8. The Spring Festival factor has caused food prices to fall sharply year-on-year. The recovery of supply and the fall in demand after the Spring Festival also led to a slowdown in the growth of food prices. The rise in consumer demand during the Spring Festival has driven food prices to rise significantly. In the week before the festival, the average wholesale price of 28 key monitored vegetables in the Ministry of Agriculture increased by 4.9% from the previous month and increased by 0.3% during the Spring Festival. The Qianhai Vegetable Price Index rose by 4.9% and 4.0% respectively before the holiday and during the Spring Festival. Fruit prices also showed an upward trend, with prices increased by 2.5% and 0.1% respectively before and during the holidays. The vegetable price of the Ministry of Agriculture and the price of Qianhai vegetable increased by 2.2% and 2.3% in January, down from 5.1% and 7.5% in December. Pork prices also entered the price increase mode during the Spring Festival. The average price of pork in 36 cities in the week before the holiday rose by 1.1%, compared with 6.34% in January, which was basically the same as 6.27% in December. According to the Ministry of Agriculture, the average wholesale price of pork during the Spring Festival continued to rise by 0.27%, compared with 2.7% in January, down from 3.2% in December. 5. Currency: raising interest rates, monetary policy continues to tighten On February 3, the central bank conducted 20 billion 7 days, 10 billion 14 days and 20 billion 28 days reverse repurchase. The winning rates were 2.35%, 2.5% and 2.65%, respectively, up 10 basis points from the previous period. The central bank announced that since February 3, 2017, the standing loan facility (SLF) rate was raised, 3.1% (originally 2.75%), 3.3 days (3.35%) in 7 days, and 3.7% (3.6%) in January. At the same time, the central bank also informed that since February 3, the local method of financial institutions that do not meet the macro-prudential requirements, the standing loan lending convenience rate plus 100 basis points, that is, overnight, 7 days, 1 month interest rates are 4.1 %, 4.35%, 4.7%. This week, the central bank’s open market operation currency was 50 billion yuan, and it was returned 120 billion yuan, with a net return of 70 billion yuan. As of February 3, the one-year government bond yield was 2.7402%, up 6.45 BP from last week; the 10-year bond yield was 3.4214%, up 7.49 BP from last week. This week, credit spreads of different maturities expanded, the credit spread of 1-year AAA corporate bonds expanded by 3.30 BP, and the credit spread of 10-year AAA corporate bonds narrowed by 3.78 BP. The depreciation of the RMB exchange rate is slightly slower. In the first week of February, the central parity of the US dollar against the yuan rose by 0.05%, the US dollar against the RMB spot exchange rate rose by 0.06%, and the offshore RMB appreciated by 0.88%. Figure 1: 30 large and medium-sized cities real estate sales fall Figure 2: Daily average coal consumption of the six major power generation in January fell year-on-year Figure 3: The price of pigs is stable, and the growth rate of vegetable prices is falling. Figure 4: Treasury yields go up Enter [Sina Finance and Economics Unit] Discussion Kids Cap,Children Cap,Custom Dad Hats,Kids Baseball Cap Dongyang City Feilong Cap Co., Ltd. , https://www.zjflcaps.com